Alternatives Database
Blood Physiology
Producer: Sheffield BioScience ProgramsThe program is divided into three sections:
1. Red Blood Cell Indices - this program simulates the determination of standard red blood cell indices, which may be performed in the laboratory using fresh blood samples, and used to produce a haematological profile.
Red blood cell count - simulated haemocytometry,
Haematocrit (PCV) - simulation of the use of an haematocrit reader
Haemoglobin (Hb) concentration - simulated spectrophotometry including the construction of a standard haemoglobin curve.
In the Methods Section the principles of each method are explained using a combination of text and imaginative graphics. Students can then simulate performing the tests on either a normal male or a normal female subject. This allows them to interactively obtain results for red cell count, PCV and [Hb] which may then be entered into a simple calculation program to give MCV, MCH and MCHC. The complete haematological profile may then be printed.
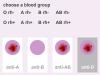
2. Blood Groups - text and graphics are used to introduce and explain the basis of the determination of ABO and Rhesus blood groups. There is then an exercise in which students can observe the interaction of a blood sample, from a subject of unknown blood group, and known antisera (anti-A, anti-B and anti-D). They are then asked to select the correct blood group from a list of possible answers. Different blood groups are generated randomly and students can try as many examples as they wish. A record of their score is kept and displayed on-screen.
3. Anaemias - Nine patient case histories are used to teach the principles of how the medical history, peripheral blood films and the results of haematological tests can contribute to diagnosis of anaemias. Each case has a brief medical history, a haematological profile (RBC count, Hb concentration, PCV, MCV, MCH, MCHC), a peripheral blood film which indicates how this differs from normal blood and the results of other blood indices. Students are required to select an appropriate diagnosis initially from one of the four main types (iron deficiency, megaloblastic, haemolytic and aplastic) and then with the aid of additional test results to further define this by selecting one from nine possible diagnoses (enzyme deficiency, thalassaemia, haemorrhage, sickle cell, bone marrow aplasia, folate deficiency, hereditary spherocytosis, vitamin B12 deficiency, autoimmune (drug induced), iron deficiency).
Language Versions: English
Recommended System Requirements:
Windows:
Microsoft Windows XP (32 bit), Windows Server 2003 (32-bit), Windows Server 2008 (32 bit), Windows Vista (32 bit), Windows 7 (32 bit and 64 bit), Windows 8
2.33GHz or faster x86-compatible processor, or Intel Atom 1.6GHz or faster processor for netbooks
128MB of RAM (1GB of RAM recommended for netbooks); 128MB of graphics memory
Internet Explorer 7.0 or later, Mozilla Firefox 4.0 or later, Google Chrome, Safari 5.0 or later, or Opera 11
Mac OS:
Mac OS X v10.6, v10.7, or v10.8
Intel Core Duo 1.83GHz or faster processor
256MB of RAM; 128MB of graphics memory
Safari 5.0 or later, Mozilla Firefox 4.0 or later, Google Chrome, or Opera 11
Target Audience: Undergraduate. Some sections may be suitable for good high school students.
Price: £250 (multiuser, educational license)